ARA
Grasshopper plugin for data-driven and inverse design methods with generative AI.
Introduction
ARA is a Grasshopper plugin that augments the design process with data-driven and inverse design approach by combining parametric models built in Grasshopper with generative AI models. It enables designers, architects and engineers to efficiently generate design solutions with the assistance of generative neural networks. The inverse design paradigm accelerates design exploration by providing many different design variants that match project objectives.
With ARA, you can easily generate a project-specific the dataset from an existing parametric model definition in Grasshopper, and then train and deploy a custom autoencoder model to generate designs that satisfy the requested target values, such as performance metrics or design constraints.
ARA also comes with various visualization tools for data analysis and performance evaluation.
ARA is open-source and builds on top of the AIXD: AI-eXtended Design toolkit.
Attention
ARA was developed for Rhino 7 on Windows. It was minimally tested on other versions of Rhino (8.0) or other operating systems (Mac).
Inverse Design
Inverse design is a design paradigm that accelerates design exploration by providing many different design variants that match requested objectives.
A parametric design model is an example of a forward design, mapping from inputs (design parameters) to outputs (peformance attributes). It can entail procedures to generate geometry, run simulations and calculate evaluation metrics.
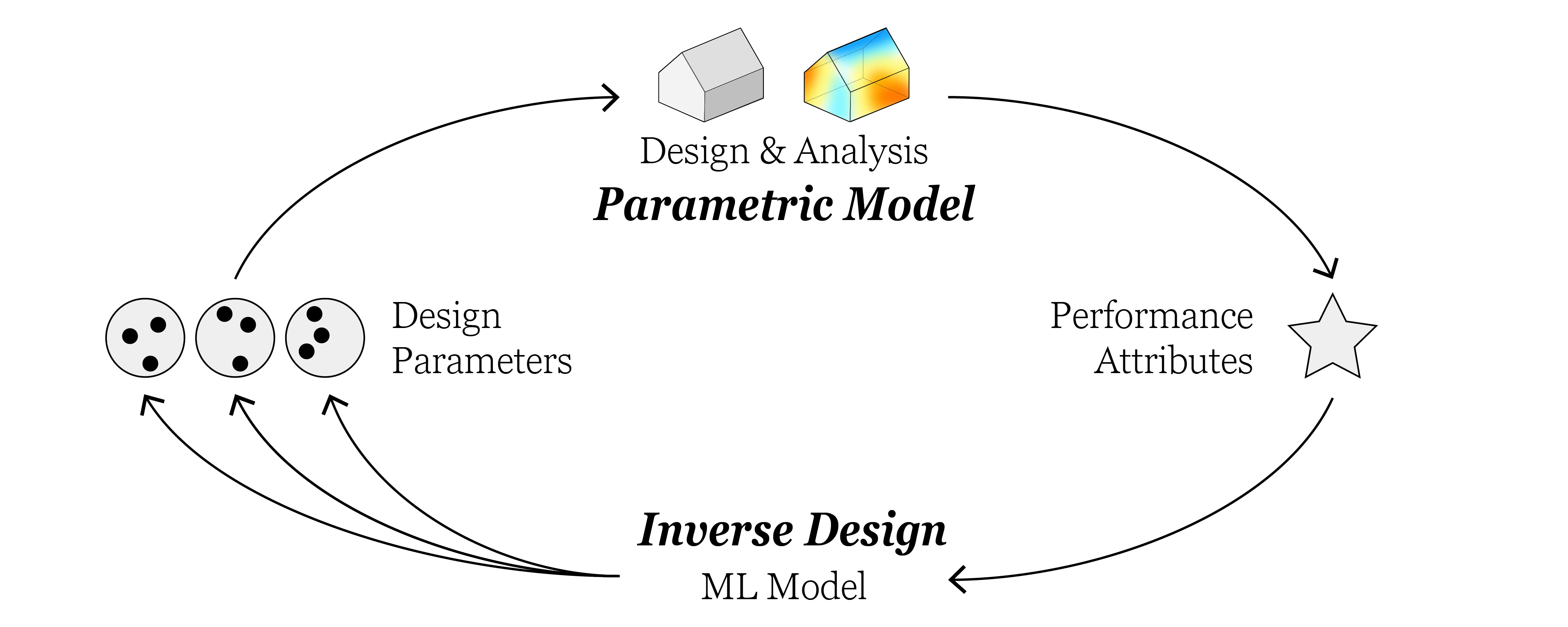
In inverse design, the process is reversed: the designer specifies the desired target values and the model generates the corresponding design parameters. In many cases, this is a one-to-many mapping, meaning that there are multiple design solutions that satisfy the target values. Being able to obtain multiple equivalent solutions may be a valuable asset in the design process to explore different design alternatives. In ARA, the inverse design process is achieved by training a conditional (variational) autoencoder model - a type of deep neural network (more details can be found here).