3.3. Planning scene and collision objects
Note
The following examples use the ROS backend and the MoveI! planner for UR5 robots. Before running them, please make sure you have the ROS backend correctly configured and the UR5 Planner started.
To plan motion paths that avoid collisions with other objects than the robot itself, the backend’s planning scene has to be updated.
This is the representation of the planning scene in RViz with the UR5.
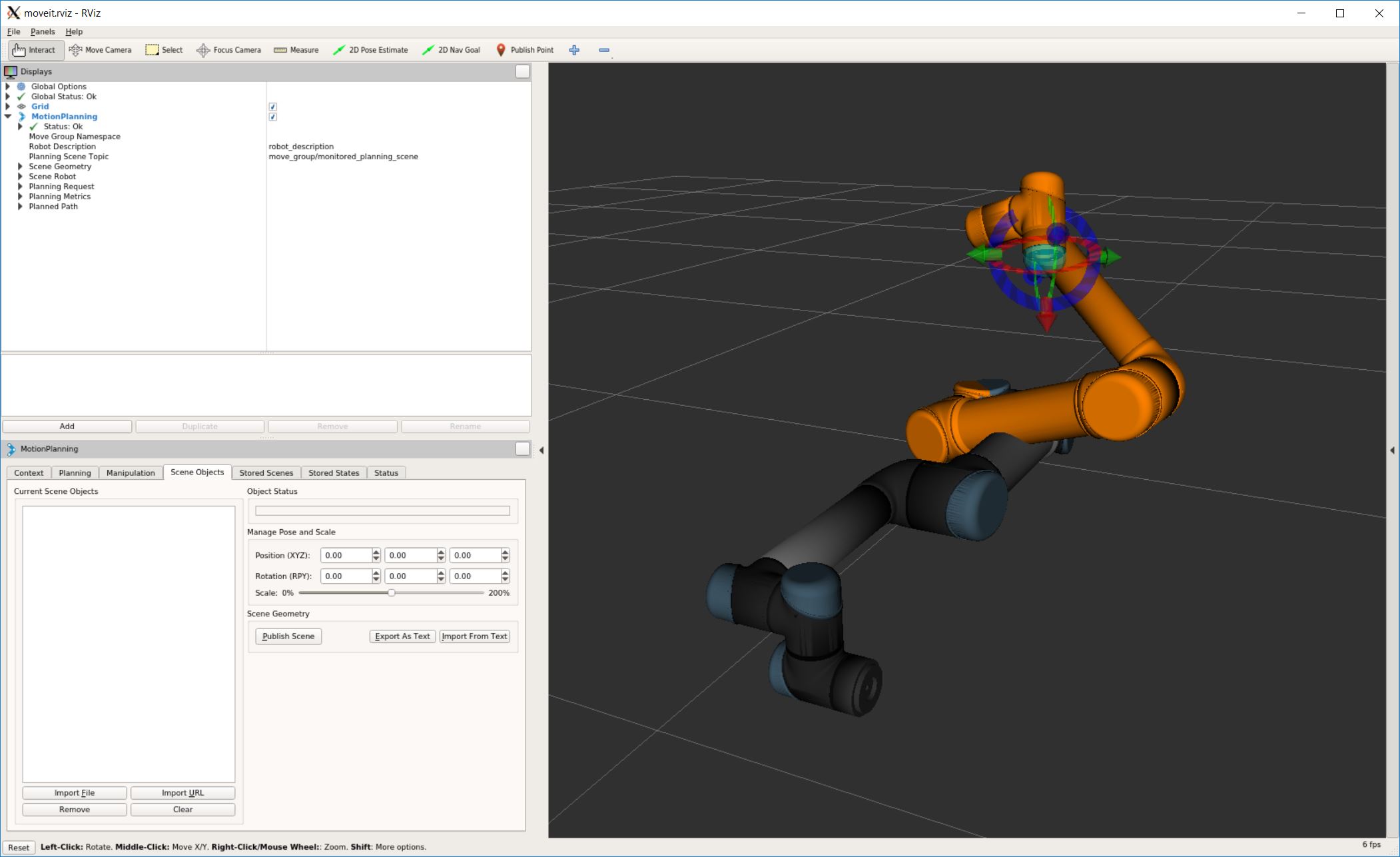
Note
If using Docker to run ROS, you can open RViz on your browser.
3.3.1. Collision meshes
The following script adds a floor to the planning scene.
import time
from compas.datastructures import Mesh
import compas_fab
from compas_fab.backends import RosClient
from compas_fab.robots import CollisionMesh
from compas_fab.robots import PlanningScene
from compas_fab.robots.ur5 import Robot
with RosClient() as client:
robot = Robot(client)
scene = PlanningScene(robot)
mesh = Mesh.from_stl(compas_fab.get('planning_scene/floor.stl'))
cm = CollisionMesh(mesh, 'floor')
scene.add_collision_mesh(cm)
# sleep a bit before terminating the client
time.sleep(1)
The backend’s updated planning scene after executing the above script.
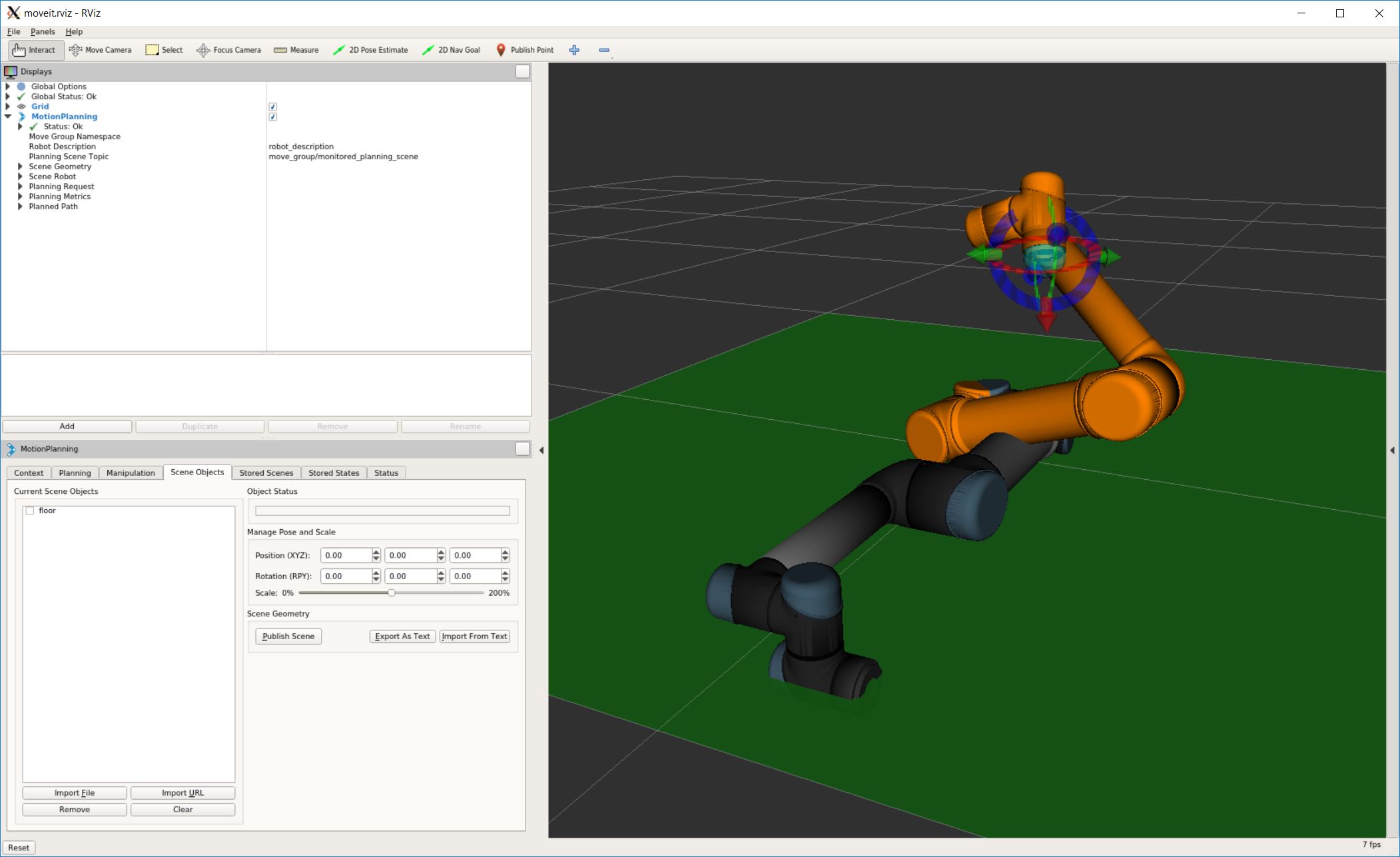
To remove the floor, use the identifier assigned when adding it:
import time
from compas_fab.backends import RosClient
from compas_fab.robots import PlanningScene
from compas_fab.robots.ur5 import Robot
with RosClient() as client:
robot = Robot(client)
scene = PlanningScene(robot)
scene.remove_collision_mesh('floor')
# sleep a bit before terminating the client
time.sleep(1)
The following script adds several boxes (bricks) to the planning scene. Here,
we use append instead of add to have multiple collision objects
clustered under the same identifier. Like that, we don’t need to keep track of
all identifiers if we later want to remove them.
import time
from compas.datastructures import Mesh
from compas.geometry import Box
from compas_fab.backends import RosClient
from compas_fab.robots import CollisionMesh
from compas_fab.robots import PlanningScene
from compas_fab.robots.ur5 import Robot
with RosClient() as client:
robot = Robot(client)
scene = PlanningScene(robot)
brick = Box.from_width_height_depth(0.11, 0.07, 0.25)
for i in range(5):
mesh = Mesh.from_vertices_and_faces(brick.vertices, brick.faces)
cm = CollisionMesh(mesh, 'brick')
cm.frame.point.y += 0.5
cm.frame.point.z += brick.zsize * i
scene.append_collision_mesh(cm)
# sleep a bit before terminating the client
time.sleep(1)
The backend’s updated planning scene after executing the above script. Note the red robot link indicating the collision.
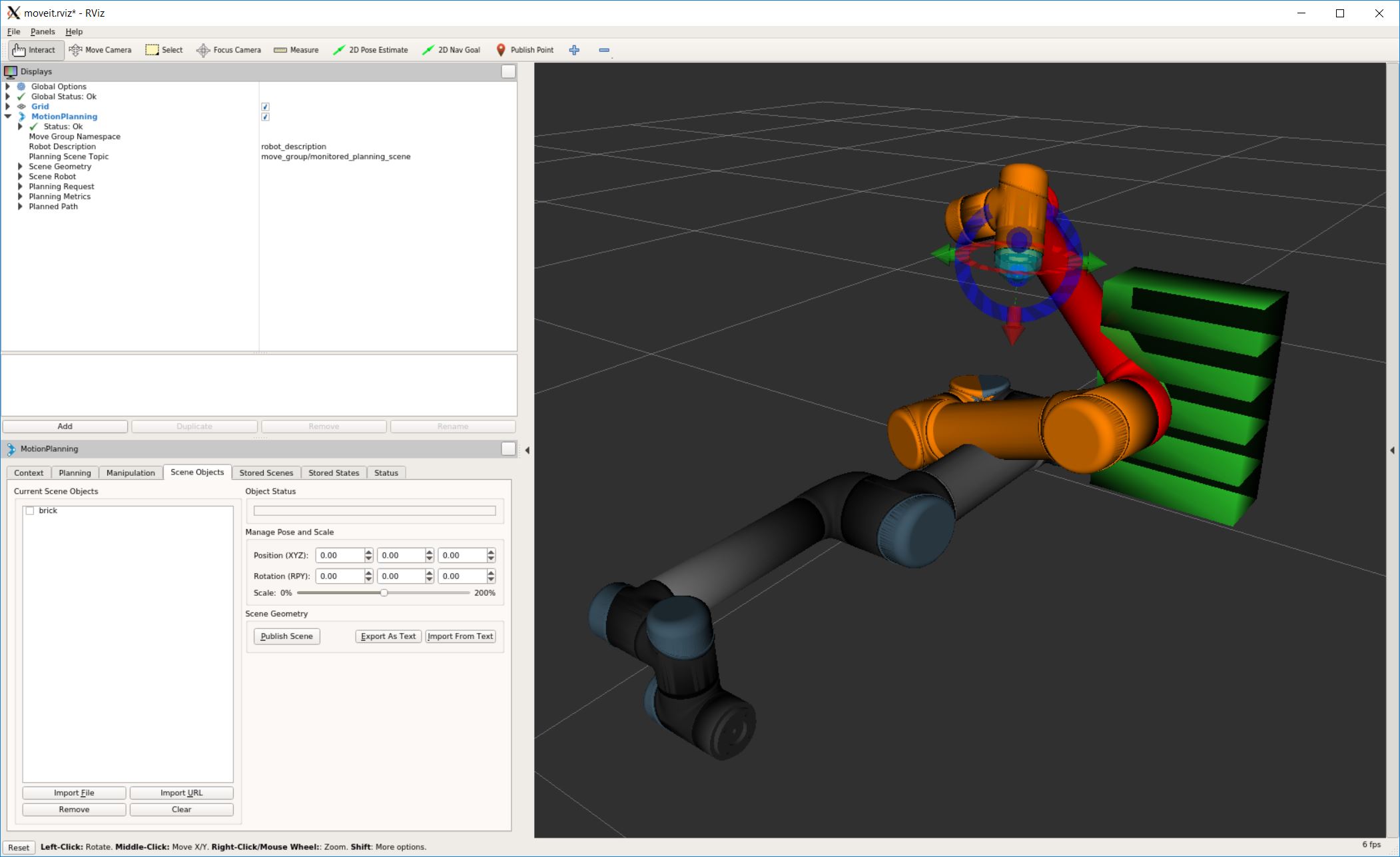
3.3.2. Attach a collision mesh to a robot’s end-effector
The following script attaches a collision mesh to the robot’s end-effector. Collision objects can be attached to any of the robot’s links.
import time
from compas.datastructures import Mesh
import compas_fab
from compas_fab.backends import RosClient
from compas_fab.robots import CollisionMesh
from compas_fab.robots import PlanningScene
from compas_fab.robots.ur5 import Robot
with RosClient() as client:
robot = Robot(client)
scene = PlanningScene(robot)
# create collison object
mesh = Mesh.from_stl(compas_fab.get('planning_scene/cone.stl'))
cm = CollisionMesh(mesh, 'tip')
# attach it to the end-effector
group = robot.main_group_name
scene.attach_collision_mesh_to_robot_end_effector(cm, group=group)
# sleep a bit before terminating the client
time.sleep(1)
The backend’s updated planning scene after executing the above script.
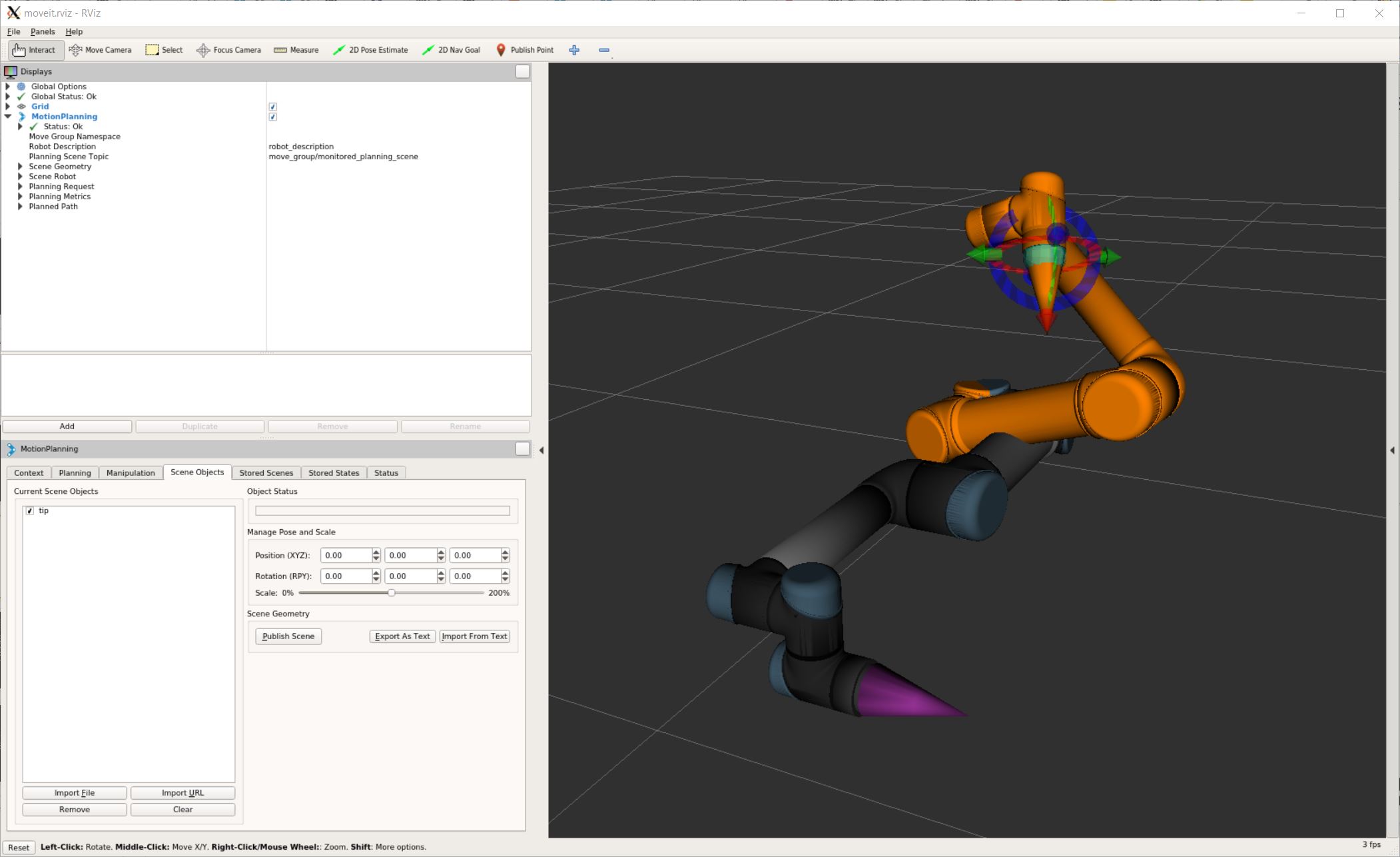
3.3.3. Plan motion with an attached collision mesh
Coming soon…